2015-CCM-ARDSnet保护性通气策略机械通气27小时肺部炎症反应持续存在且分布在非重力依赖区

Crit Care Med 2015; 43:e123–e132
ARDSnet保护性通气策略机械通气27小时肺部炎症反应持续存在且分布在非重力依赖区
谈莉 刘松桥翻译,邱海波审校
【目的】[18F]FDG PET可反映细胞代谢,在肺炎症反应时主要反映中性粒细胞活跃性,可用于体内区域性肺炎症反应的研究。我们旨在通过PET图像研究ARDS猪模型给予ARDS Network推荐的肺保护性通气策略72小时后,炎症反应的部位和进展,及其与CT反映的形态学之间的关系。
Objective: PET with [18F]fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose can be used to image cellular metabolism, whichduring lung inflammation mainly reflects neutrophil activity, allowing thestudy of regional lung inflammation in vivo. We aimed at studying the locationand evolution of inflammation by PET imaging, relating it to morphology (CT),during the first 27 hours of application of protective-ventilation strategy assuggested by the Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network, in a porcineexperimental model of acute respiratory distress syndrome.
【设计】前瞻性动物实验研究。
Design: Prospective laboratory investigation.
【地点】大学动物实验室。
Setting: University animal research laboratory.
【对象】10只小猪复制ARDS模型。
Subjects: Ten piglets submitted to an experimental model of acute respiratorydistress syndrome.
【方法】通过肺灌洗后给予低PEEP、高吸气压的损伤性机械通气210分钟复制ARDS模型,随后按照ARDS Network推荐的通气策略给予控制通气直至27小时,在此期间间隔24小时记录动态[18F]FDG PET摄取图像。
Interventions:Lunginjury was induced by lung lavages and 210 minutes of injurious mechanicalventilation using low positive end-expiratory pressure and high inspiratorypressures. During 27 hours of controlled mechanical ventilation according toAcute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network strategy, the animals were studied withdynamic PET imaging of [18F]fluoro-2-deoxyd- glucose at two occasions with 24-hour interval betweenthem.
【监测指标和主要结果】计算全肺、从上至下的四个水平肺组织区域(非重力依赖区至重力依赖区)和按标准HU分类法进行肺组织分区的局部肺组织[18F]FDG摄取率。在机械通气第3小时和第27小时,全肺的[18F]FDG摄取率均明显增加,提示肺部存在持续的炎症反应,且非重力依赖区[18F]FDG摄取率高于重力依赖区(p=0.002和p=0.006)。与机械通气3小时相比,机械通气27小时 [18F]FDG摄取率的区域性分布也发生了改变(p=0.003),[18F]FDG摄取率提示炎症更显著集中在非重力依赖区,且27小时后低通气区肺组织摄取率最高。
Measurementsand Main Results: [18F]fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose uptake rate was computed for the total lung,four horizontal regions from top to bottom (nondependent to dependent regions) andfor voxels grouped by similar density using standard Hounsfield unitsclassification. The global lung uptake was elevated at 3 and 27 hours,suggesting persisting inflammation. In both PET acquisitions, nondependentregions presented the highest uptake (p = 0.002 and p = 0.006). Furthermore, from 3 to 27 hours, there was achange in the distribution of regional uptake (p = 0.003), with more pronounced concentration ofinflammation in nondependent regions. Additionally, the poorly aeratedtissue presented the largest uptake concentration after 27 hours.
【结论】在肺损伤给予机械通气27小时,ARDS Network推荐的肺保护性通气策略不能减轻全肺的炎症反应,导致炎症集中在非重力依赖区及低通气区域。研究表明在ARDS Network的通气策略实施过程中,低通气区域是炎症反应发生发展的重要部位。
Conclusions: Protective Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Networkstrategy did not attenuate global pulmonary inflammation during the first 27hours after severe lung insult. The strategy led to a concentration ofinflammatory activity in the upper lung regions and in the poorly aerated lungregions. The present findings suggest that the poorly aerated lung tissue is animportant target of the perpetuation of the inflammatory process occurringduring ventilation according to the Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Networkstrategy. (Crit Care Med 2015; 43:e123–e132)
【关键词】[18F]FDG;急性肺炎症反应;急性呼吸窘迫综合征;机械通气;正电子成像术;呼吸机相关性肺损伤
Key Words: [18F]fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose; acute pulmonary inflammation;acute respiratory distress syndrome; mechanical ventilation; positron emission tomography;ventilator-induced lung injury
表1 肺气体交换,血流动力学和呼吸力学指标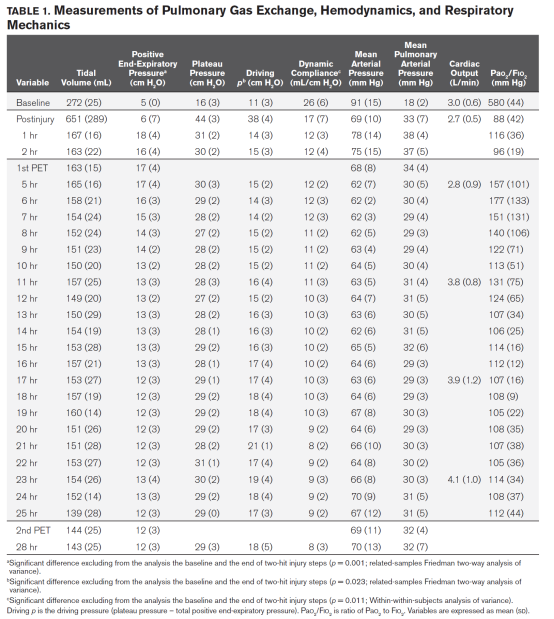
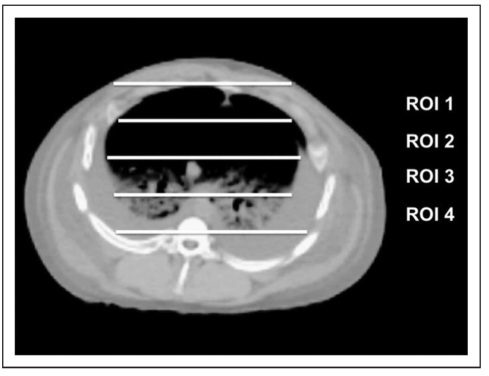
图1 从腹侧(上)到背侧(下)垂直将肺分为四个区域(ROIs)
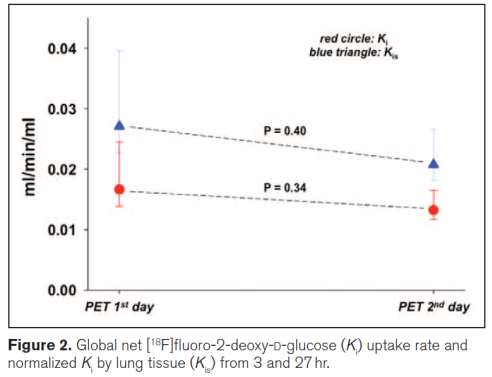
图2 机械通气第3小时和第27小时全肺组织[18F]FDG摄取率(红色圆)和标化的每克肺组织[18F]FDG摄取率(蓝色三角)
Ki =[18F]FDG摄取率 (18F-FDG netuptake rate)
Kis = 标化每克肺组织[18F]FDG摄取率 (Proportional to18F-FDG uptake per gram of lung tissue normalized Ki by lung tissue),computing a specific Ki as Kis = Ki/Ftissue, where Ftissuerefers to lung tissue fraction and equals 1 – lung gas fraction (Fgas)as calculated from the CT
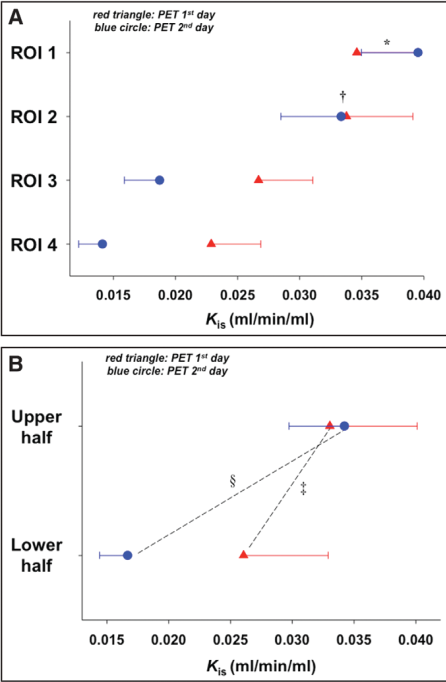
图 3机械通气第3小时和第27小时局部区域肺组织标化的每克肺组织[18F]FDG摄取率
A机械通气第3小时和第27小时从腹侧到背侧垂直四个局部区域肺组织标化的每克肺组织[18F]FDG摄取率
B 采用同一个截面上下两个部分进行局部区域肺组织标化的每克肺组织[18F]FDG摄取率
*单因素方差分析显示27小时机械通气后ROI 1区肺组织[18F]FDG摄取率明显高于其他各区域
†单因素方差分析显示27小时机械通气后ROI 2区肺组织[18F]FDG摄取率明显高于其他各区域
‡单因素方差分析显示3小时机械通气后腹侧肺组织[18F]FDG摄取率与背侧差异有显著统计学意义
§单因素方差分析显示27小时机械通气后腹侧肺组织[18F]FDG摄取率与背侧差异有显著统计学意义
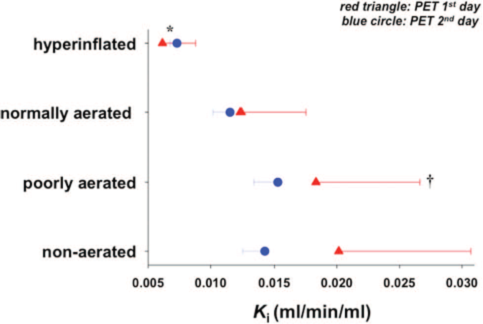
图4机械通气第3小时和第27小时不同通气状态肺组织[18F]FDG摄取率
根据CT值判定区域肺组织的通气情况:过度膨胀区,hyperinflated
ROI (CT灰度值 –1000 到 –901HU); 正常通气区normally aerated ROI (CT灰度值–900 到 –501 HU); 低通气区poorly aerated ROI (CT灰度值–500 到 –101 HU); 肺泡塌陷区 collapsed (i.e., 无通气区nonaerated)
ROI (CT灰度值 –100 到+100 HU).
*过度通气区[18F]FDG摄取率明显低于其他各区域.
†低通气区[18F]FDG摄取率明显高于其他各区域.
表2整肺组织[18F]FDG摄取率,从腹侧到背侧四个水平区域肺组织[18F]FDG摄取率
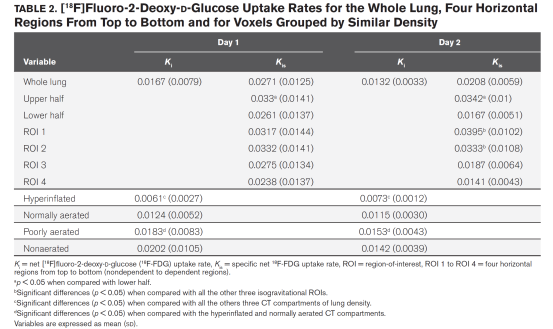

图5 同一只猪机械通气27小时后两个不同横截面的[18F]FDG摄取率,与同期CT进行比较(呼气相)
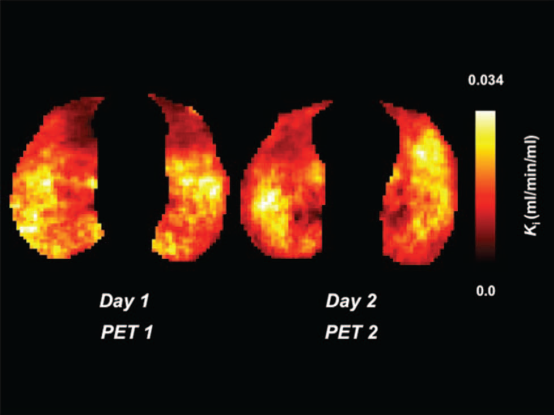
图6同一只猪机械通气第3小时和第27小时后的[18F]FDG摄取率比较